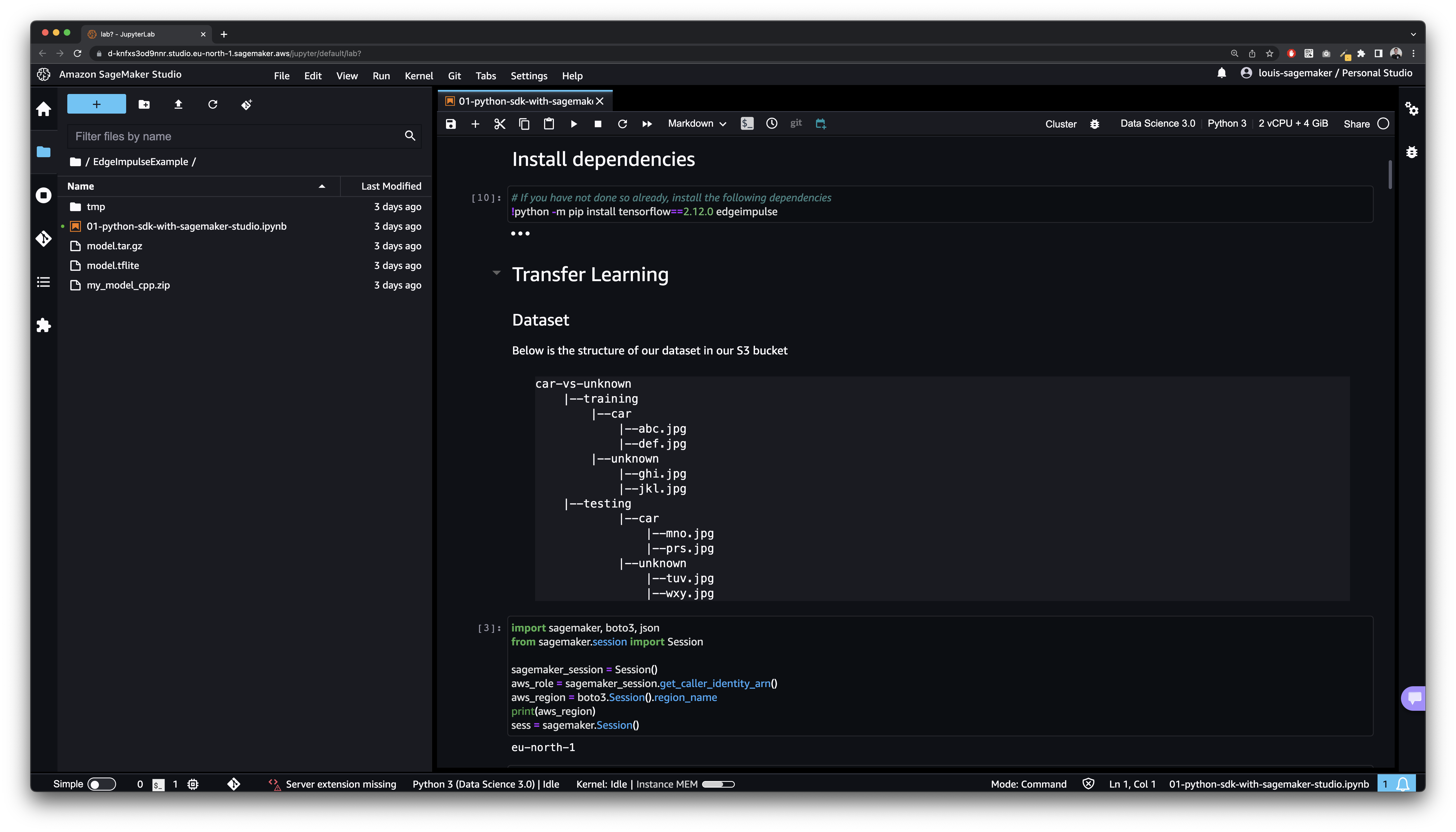
SageMaker Studio
- The
Python 3 (Data Science 3.0)kernel was used. - We used a dataset to classify images as
carvsunknown. - The dataset has been imported in the Edge Impulse S3 bucket configured when creating the SageMaker Studio domain. Make sure to adapt to your path or use the AWS reference project.
- The training instance used is
ml.m5.large.
Install dependencies
Transfer Learning
Dataset
Below is the structure of our dataset in our S3 bucket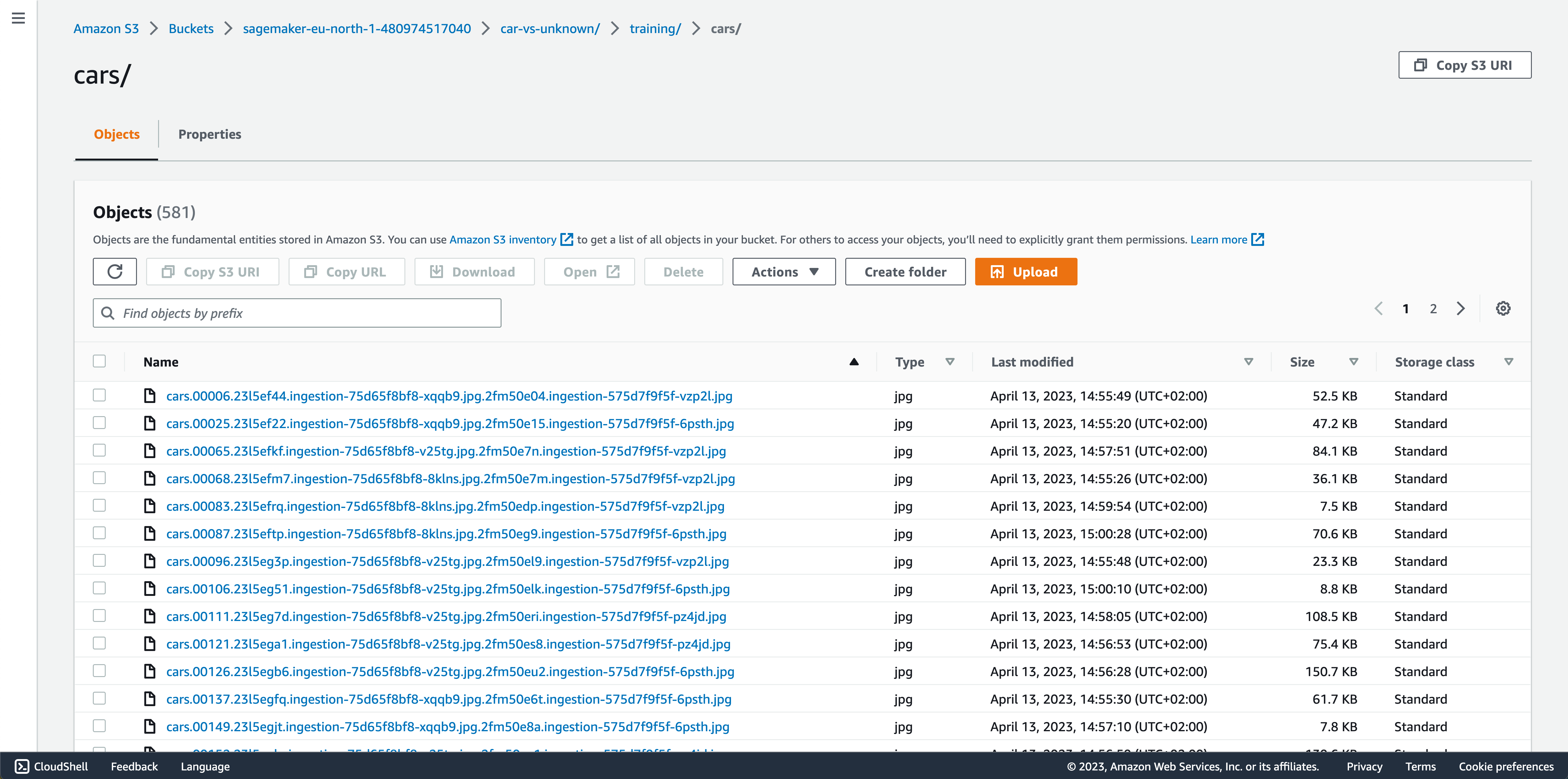
S3 Bucket overview
Train
You can continue with the default model, or can choose a different model from the list. Note that this tutorial has been tested with MobileNetv2 based models. A complete list of SageMaker pre-trained models can also be accessed at Sagemaker pre-trained Models.Retrieve and prepare the newly trained model
Edge Impulse
You will need to obtain an API key from an Edge Impulse project. Log into edgeimpulse.com and create a new project. Open the project, navigate to Dashboard and click on the Keys tab to view your API keys. Double-click on the API key to highlight it, right-click, and select Copy.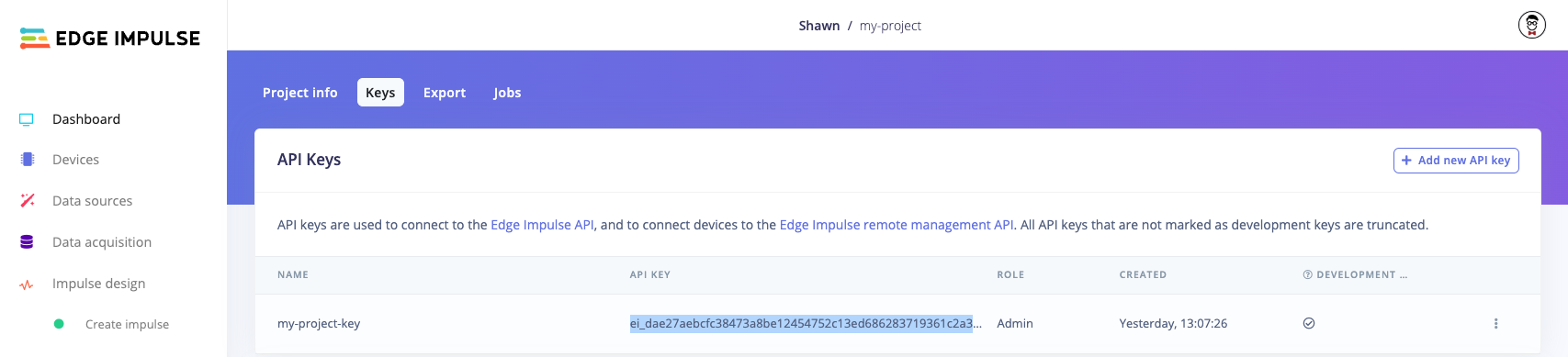
Copy API key from Edge Impulse project
ei.API_KEY value in the following cell:

